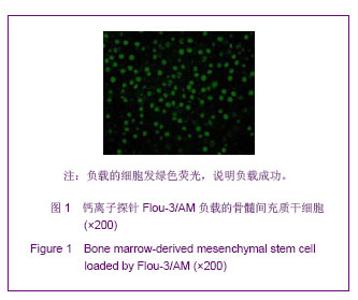
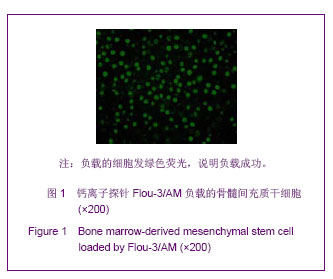
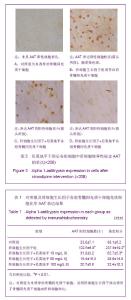
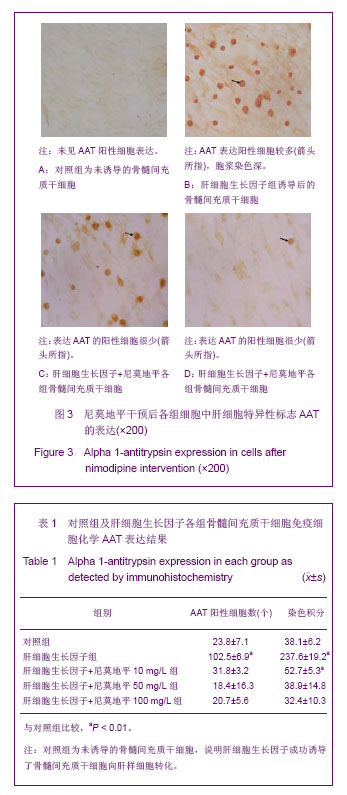
| [1]裴雪涛.干细胞技术[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2002.
[2]Bianco P, Riminucci M. Bone marrow stromal cells:nature, biology and potential application.Stem Cells.2001; 19(3): 180-192.
[3]Mertelsmann R.Plasticity of bone marrow derived stem cells.Hematother Stem Cell Res.2000;9(6):957-960.
[4]Feng Z, Li C, Jiao S, et al.In Vitro Differentiation of Rat Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Hepatocytes. Hepato-Gastroenterology 2011; 58: 2081-2086.
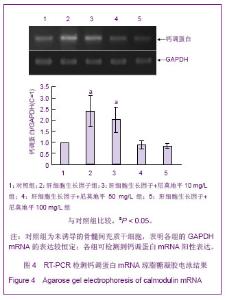
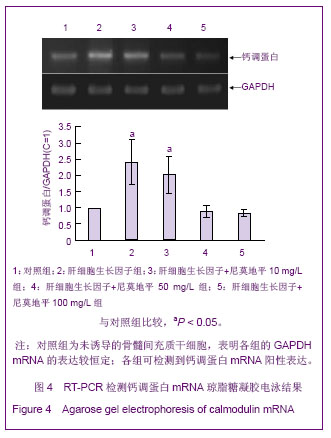
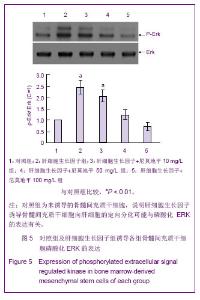
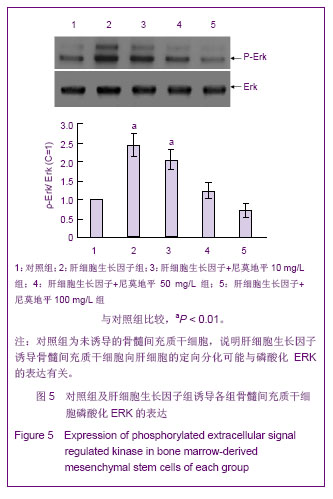
[5]赵林,冯智慧,焦淑贤全骨髓贴壁法分离培养大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞及其生物学特性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(32):5923-5927.
[6]Baksh D,Song L,Tuan RS.Adult mesenehymal stem cells:charaeterization , differeniiation and application in cell and gene therapy.J Cell Mol Med. 2004;3:301-316.
[7]Kang XQ, Zang WJ, Bao LJ, et al.Fibroblast growth factor-4 and hepatocyte growth factor induce differentiation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes.World J Gastroenterol.2005;11:7461-7465.
[8]Berridge MJ,Bootman MD.LIPPP. Calcium: alifeanddeathsignal. Nature. 1998;395:645-648.
[9]Brown EM, Vasiler PM, Hebert SC.Caleium ions as extracellular messengers. Cell. 1995;83:679-82.
[10]Bers DM, Perez-Reyes E. Ca2+ channels in cardiac myocytes: structure and function in Ca2+ influx and intracellular Ca2+ release. Cardiovasc Res.1999;42:339-360.
[11]Delbridge LM, Satoh H, Yuan W, et al. Cardiac myocyte volume, Ca2+ fluxes, and sarcoplasmic reticulum loading in pressure-overload hypertrophy. Am J Physiol.1997;272: H2425-2435.
[12]Distelhorst C W, McCormick TS. Bcl-2 acts subsequent to and independent of Ca2+ fluxes to inhibit apoptosis in thap sigargin and glucocortico id-treatedmouse lymphoma cells. Cell Calcium. 1996;19(6):473-483.
[13]Moldentin JD, Lu J R, Antos CL, et al. A calcineurint ranscriptional pathway for cardiac hypertrophy. Cell.1998;93: 215-228.
[14]Vargas GA, Hoeflich A, Jehle PM: Hepatocyte growth factor in renal failure: promise and reality. Kidney Int.2000; 57(4):1426- 1436.
[15]Kao JP, Harootunian AT.Tsien RY. Photochemically genetated eytosolic calcinm pulses and their detection by flou-3.J Biol Chem 1989;264:8179-8184. |